Radioactive indicators in surface waters of the Ploučnice river basin
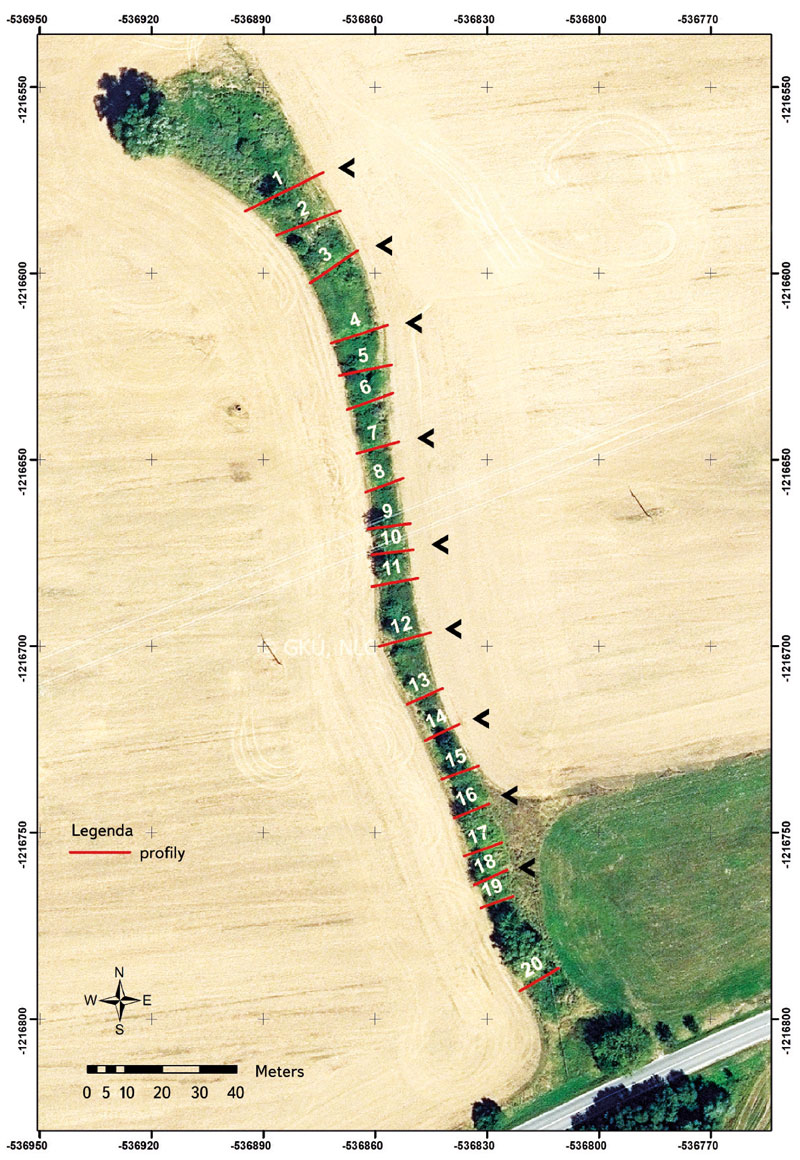
The Czech Hydrometeorological Institute (CHMI) is engaged in systematic monitoring and evaluation of radiological indicators in surface waters. The article describes changes in the values of radiological indicators in surface waters in the time series from 1967 to the present. The evolution of total volume alpha and beta activity, uranium concentration, and radium activity (226Ra) is described on characteristic profiles in the area of uranium-containing raw materials mining, in the vicinity of Stráž pod Ralskem, where the mining of radioactive raw materials has already been suppressed. The Ploučnice river flows through this mining area and flows into the Elbe river in Děčín near the Hřensko border crossing, where activities of radiological indicators are also monitored and documented. Following the cessation of uranium mining at the Stráž pod Ralskem deposit, uranium concentrations dropped by two orders of magnitude, and surface waters on the Ploučnice – Mimoň profile have been classified as Class I – unpolluted water for the last five years. The values of Kendall’s correlation coefficient τ for the profiles evaluated on the selected profiles during the mining period are characterized by an increasing trend (+0.7) for the indicator of total volume beta activity; after the end of mining, a decreasing trend is indicated (-0.5).