The impact of hydrological extremes on ponds and small water reservoirs
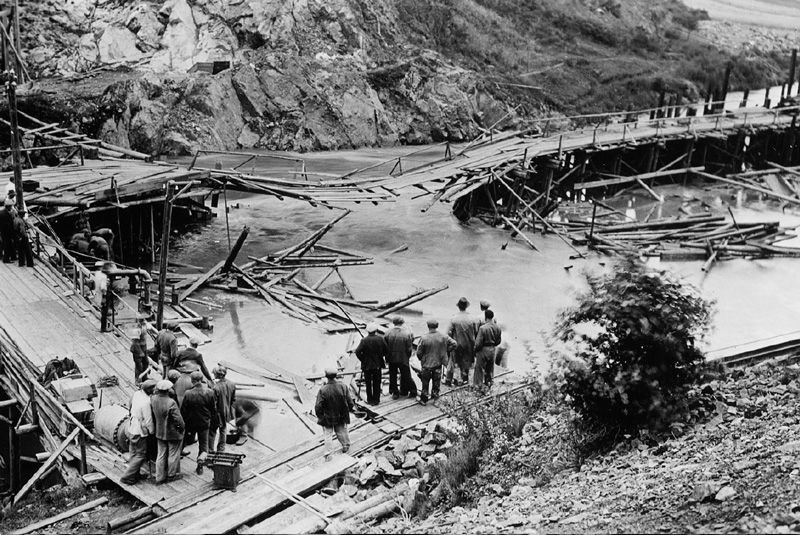
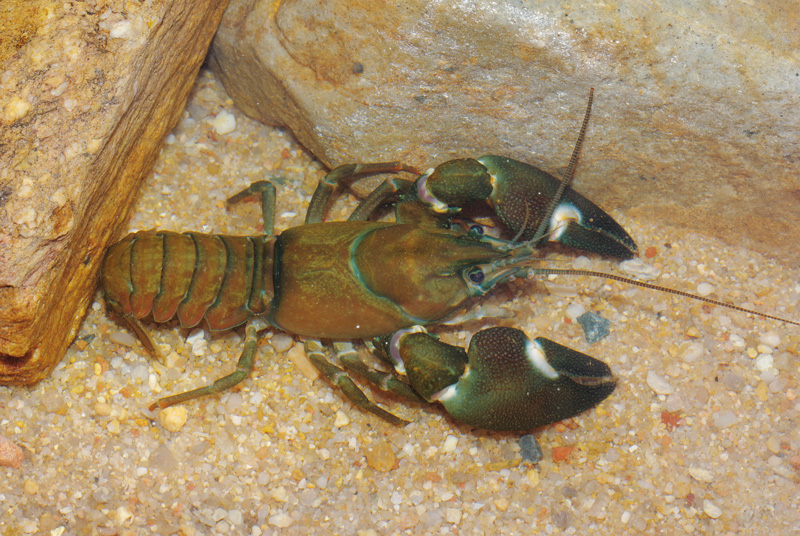
This paper presents the methodological approach and key results of the research project Design of ponds and small reservoirs in terms of the possibility to comply with MPF and flood safety (TA CR, no. SS03010230). The project focused on the assessment of ponds, pond systems and small reservoirs in relation to two hydrological extremes – draught and floods. During periods of drought, the issue of maintaining the minimum residual flow is addressed. The article describes the method of determining and maintaining the minimum residual flow at these hydraulic structures. Furthermore, the article deals with the assessment of the security of these structures in terms of the safe discharge of flood flows in accordance with ČSN 75 2935 – Assessment of the safety of hydraulic structures during floods.