Old groundwater in hydrogeological regions 4410 and 4522
The article presents a project from the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic dealing with the hydrogeology of old waters in hydrogeological regions 4410 and 4522. The aim of the paper is to present a brief hydrogeological characterization of the area of interest, to present the results after the first year of the project, and to describe the uncertainties of existing information. Old groundwaters that have negligible concentrations of tritium can be considered a strategic resource because they are less susceptible to current contamination.
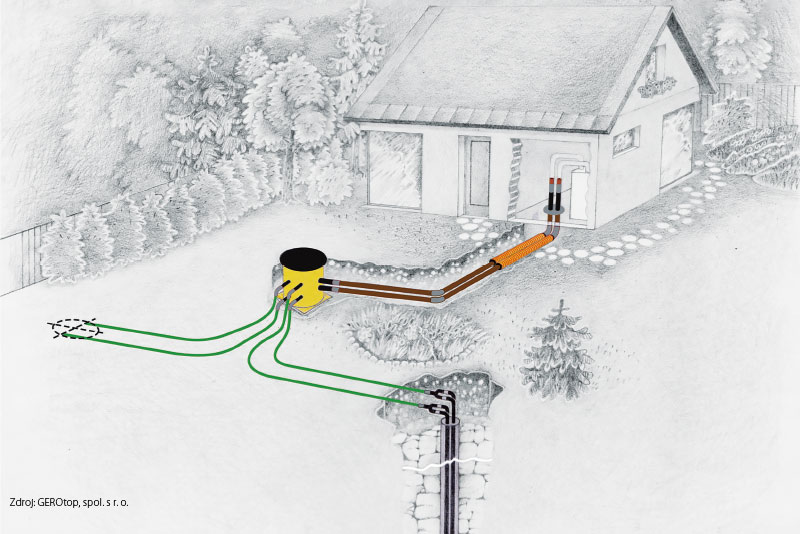
Hydrogeological aspects of boreholes for heat pumps
In recent years, there have been significant legislative and methodological changes in the construction and use of geothermal heat pumps (GHP), also known as ground-source heat pumps (GSHPs). The use of GHP has become a widespread
solution for heating buildings of all kinds, from family homes to industrial buildings. This article concerns GHP (ground-to-water and water-to-water types) that use shallow geothermal energy, obtained mainly through boreholes.
„Water Centre“
The research project of the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic SS02030027 „Water systems and water management in the Czech Republic in conditions of climate change“, whose guarantor is the Ministry of the Environment, tries to answer the question of whether we will continue to have enough quality water. Climate change and the associated drought, as well as human behaviour and demands threaten water, and solutions must be sought for the immediate future.
Estimation of natural groundwater resources in hydrogeological zones in the Czech Republic under changing climatic conditions 1981–2019
In the Czech Republic, hydrogeological zones were defined as early as 1965 as a part of the regional hydrogeological survey. A hydrogeological zone (HGZ) is defined as a unit with similar hydrogeological conditions, defined tectonically and geologically, in whose territory a certain type of aquifer and groundwater circulation prevails. The boundaries of HGZs have been modified over time and their numerical hydrogeological characteristics have been determined by various methods; one of the basic characteristics is the amount of natural groundwater resources. Natural resources are the dynamic component of groundwater and are expressed in m3.s-1. They are determined by the recharge of water to the aquifer system (precipitation, groundwater overflows from other aquifers, natural infiltration of surface water, etc.). If the HGZ is hydrogeologically closed, the long-term average of its recharge from precipitation and the long-term average of baseflow can be used as an estimate of the natural groundwater resource. In the “Groundwater Rebalance Project”, estimates of natural groundwater resources in 152 hydrogeological zones in the Czech Republic were processed and are presented in the report [1]. The natural resources were determined by several different methods using data from 1971–2010 and 2000–2010.
Vertical distribution of radioactive caesium-137 in soil
In the past, the environment of the Czech Republic was contaminated with anthropogenic radionuclides as a result of atmospheric nuclear weapon testing and the Chernobyl accident. The paper summarises results of vertical migration of 137Cs in soil in selected sites, performed as part of collecting data for ground water vulnerability assessment. Three sites with a different land cover were included (forest, meadow and arable land). In order to determine vertical migration of anthropogenic radionuclides, soil samples were collected up to the depth of 100 cm and subsequently analysed using the gamma-ray spectrometry.
Groundwater formation in urban areas regarding peripheral parts of Prague
Groundwater is an integral part of the hydrosphere and hydrological cycle in a healthy landscape, which is better able to withstand hydrological extremes such as floods or prolonged drought. The main source of groundwater is precipitation. There are a number of barriers for infiltration in urban areas – urban and industrial buildings, as well as increasing areas with impermeable surfaces. The aim of the paper is to draw attention to the importance of groundwater in the urban landscape and to possible measures to support the infiltration of precipitation.
The research took place in the territory of outer Prague, where there is an intensive expansion of the built-up area, which is accompanied by a lower infiltration of precipitation, compared to the open landscape. Based on the evaluation of pedological, geological and hydrogeological conditions of the area, a methodology for evaluating the suitability of the area for infiltration was developed. Based on it, two types of maps were created: an infiltration potential map evaluating primarily the permeability of the soil and rock environment, and an infiltration capacity map, in addition emphasizing the size of the free storage volume for infiltrated water. Maps are available for viewing in the map application on the project website heis.vuv.cz/projekty/praha-adaptacniopatreni.
Project CZ.07.1.02/0.0/0.0/16_040/0000380 “Analysis of adaptation measures to mitigate impacts of climate change and urbanization on the water regime in the area of external Prague”
This article is available in Czech only. For translation or more information on this topic, please contact author. Rádi bychom vás seznámili se základními údaji o projektu, který byl řešen v období 2018–2020 v rámci operačního programu Praha – pól růstu. Za tímto textem jsou pak uvedeny články zabývající se již specifickými tématy, jež byla… Read more »
Environment for life program and projects solved in TGM WRI
Environmental protection is one of the important societal needs. Appropriately oriented applied research is also necessary for its fulfillment.
Warning system for the Prague water system against micro-pollutant pollution
Physicians with a little exaggeration claim that a healthy person does not exist, only to be met with a poorly-diagnosed patient. This claim can also be applied to drinking water and wastewater.
Specifics of local water resources in supplying the population with drinking water
The paper summarizes the „Methodology for comprehensive management of small water resources to ensure optimal quality of drinking water in normal and emergency situations“ that is a main result of the research project supported by the Technology Agency of the Czech Republic (TA 02020184).