PFAS in surface waters in the Czech Republic
Per- and polyfluorinated compounds (PFAS), a group of fluorinated compounds of anthropogenic origin, have been classified as a persistent organic substances of significant concern due to their chemical properties, widespread use in a number of industrial sectors, environmental spread, long term bioaccumulation potential, and resulting risk to human health. This article brings an overview of current knowledge about the occurrence of PFAS in the environment, mainly in surface, ground, and drinking water and about the methods of their removal from con-taminated water. Furthermore, the legislative requirements regarding PFAS at the level of the EU and Czech Republic are summarised here, including the list of compounds according to the Directive of the European Parliament and the Council 2020/2184 and the Proposal for a Directive of the European Parliament and the Council 2008/105/EC.
Wastewater analysis as a tool for investigating drug abuse in education institutes
The wastewater based epidemiology (WBE) approach to wastewater has long been used for monitoring drug consumption, especially in urban agglomerations. In this pilot project, it was applied to detect drug use in selected educational establishments. The tests took place in both primary (age 6–15) and secondary schools (age 12–19). The focus was on illicit drugs (marijuana, methamphetamine, amphetamine, cocaine, and ecstasy), as well as the licit drug nicotine and its metabolites. Ephedrine was also monitored. Grab samples were taken before the start of classes between 7:30 and 8:05 a.m., and during the so-called big break, i.e., between 9:30 and 10:00 a.m., or 10:30–11:00 a.m.
Sampling was carried out on two dates, at the beginning of June and at the end of September/beginning of October 2022. There were positive find-ings for THC, ephedrine, methamphetamine and nicotine metabolites, primarily trans-3-hydroxy-cotinine. In accordance with the possibilities of the pilot project, the number of monitored schools was very small. In order to objectively determine the situation in educational facilities, it would be appropriate to monitor a more representative group, which would include, for example, vocational schools. It is also worth considering another method of sampling wastewater, e.g., several hours’ composite samples. However, in many educational institutions, this method may not be feasi-ble.
Wastewater based epidemiology, determination of selected illicit drugs and Covid-19 pandemic
The World Health Organization (WHO) declared an outbreak of a global health emergency on 30th January 2020 and a pandemic caused by Covid-19 in March of the same year. In our paper, we tried to find out if and how this situation affected drug consumption from the perspective of wastewater analysis. We compared the results of weekly sampling events from 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2022, which took place at approximately the same period of the year, but in 2020, 2021, and 2022 were affected by the state of emergency and other pandemic-related measures. We monitored the concentration of selected drugs – THC, methamphetamine, MDMA, cocaine, and some of their metabolites (amphetamine and benzoylecgonine) in wastewater samples taken at the inflow to wastewater treatment plants. According to our measurements, virtually all monitored drugs experienced changes in their consumption.
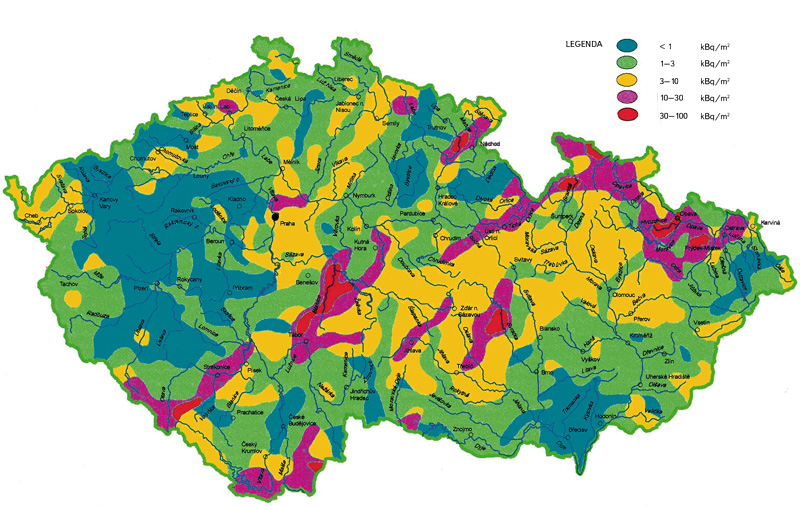
Vertical distribution of radioactive caesium-137 in soil
In the past, the environment of the Czech Republic was contaminated with anthropogenic radionuclides as a result of atmospheric nuclear weapon testing and the Chernobyl accident. The paper summarises results of vertical migration of 137Cs in soil in selected sites, performed as part of collecting data for ground water vulnerability assessment. Three sites with a different land cover were included (forest, meadow and arable land). In order to determine vertical migration of anthropogenic radionuclides, soil samples were collected up to the depth of 100 cm and subsequently analysed using the gamma-ray spectrometry.
Impact of the Nuclear power plant Temelín on concentration of selected radionuclides in the hydrosphere
The paper presents results and interpretation of long-term monitoring of occurrence and behaviour of selected radionuclides in the vicinity of the Temelín Nuclear Power Plant (Temelin NPP).
Determination of selected illicit drugs in wastewater using liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry
The wastewater-based epidemiology approach to the analysis of illicit drugs was conceptualized in 2001 and for the first time was applied in 2005 for cocaine estimation in Italy. Further, other illicit drugs as heroine, cannabis and amphetamine have been estimated.
Municipal wastewater as a diagnostic medium of the City of Prague
The article informs about regular, almost two-year long monitoring of municipal wastewater at selected sampling points of the Prague sewerage network. Selected illicit drugs (e.g. methamphetamine, MDMA, THC, cocaine), nicotine and its metabolites and the ethanol metabolite ethyl sulphate are monitored in municipal wastewater.
Determination of low level tritium concentrations for tritium tracing applications
Past tests of nuclear weapons in the atmosphere, nuclear energy facilities and tritium of natural origin are main sources of tritium in the environment. Thanks to its presence in environment and its favourable properties, tritium is used as a radiotracer.
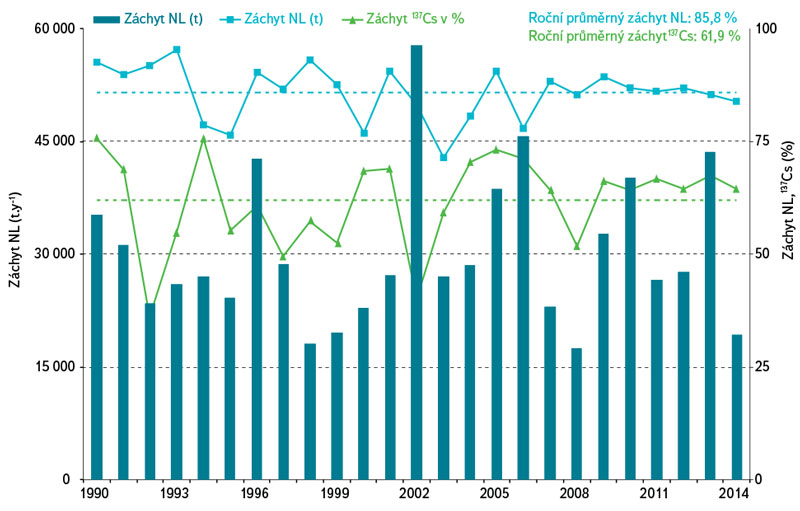
Development of selected radionuclides in surface water in the vicinity of the Temelín Nuclear Power Plant in the period 1990–2016
The paper presents results and interpretation of long-term monitoring of occurrence and behaviour of radioisotopes 3H, 90Sr and 137Cs in surface water in the vicinity of the Temelín Nuclear Power Plant. 3H, 90Sr and 137Cs originate predominantly from residual contamination due to atmospheric nuclear weapons tests and the Chernobyl disaster in the last century.
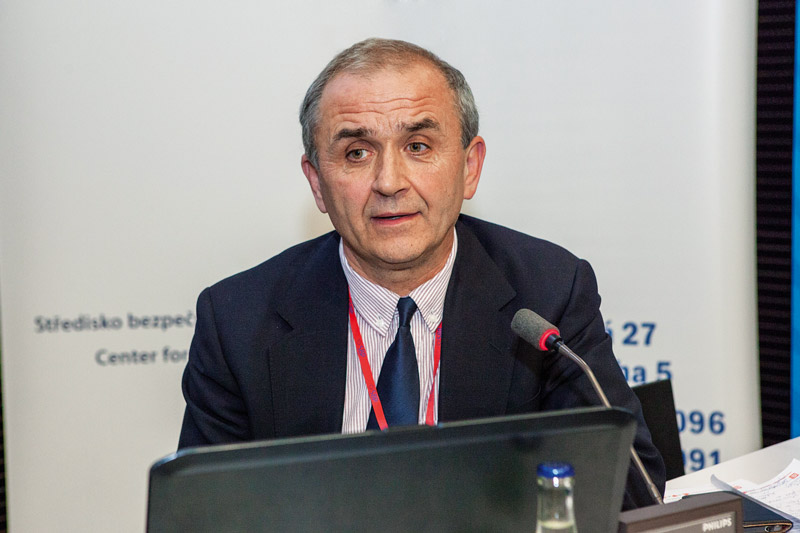
Interview with Ing. Jiří Hůlka, Deputy of the National Radiation Protection Institute, p.r.i., in the field of research and development
Interview with deputy research and development Ing. Jiří Hůlka of the National Radiation Protection Institute, which is a public research institution since 2011, when it was established by the decision of the chairman of the State Office for Nuclear Safety. The interview deals with radiation protection and public research institutions and their issues.
Cooperation of Water Research Institute and Povodí companies, state enterprise within the framework of radiation monitoring network of the Czech Republic
The paper sums up the legislative framework and cooperation of TGM Water Research Institute and Povodí companies, state enterprises.
Concentration of artificial radionuclides in hydrosphere affected by Temelín Nuclear Power Plant
Temporal and spatial changes in concentrations of selected radionuclides (tritium, radiostrontium and radiocaesium) were assessed in the parts of the Vltava and Elbe river basins affected by the operation of the Temelín Nuclear Power Plant.