HYMOD-KZ database and deficit areas
This article describes the HYMOD-KZ database, available at https://shiny.vuv.cz/HYMOD-KZ/. The database provides detailed results of hydrological modelling and hydrological balance analysis of catchments (water bodies) for current and future climate conditions; it also includes updated deficit areas, the description of which is part of this article. This tool can serve as a foundation for water management ex-perts, academia, and the broader professional community as it provides outputs at the spatial resolution of water bodies. The graphical rep-resentation of results facilitates understanding of complex hydrological phenomena and supports decision-making in water management planning.
Drought warning system and local threshold limits
Droughts and floods are extreme hydrological phenomena that are currently increasing in frequency due to the growing impact of climate change, and can have significant effects on our lives. Within the “PERUN” research project, an assessment of drought conditions and their development in the Czech Republic is being developed, along with the innovation of the warning system by the Czech Hydrometeorological Institute (CHMI). Drought is a natural phenomenon characterized by a gradual onset, long duration, and low dynamics, which requires a specific approach. The amendment to the Water Act introduces the obligation of regular reporting on drought and the establishment of a predictive service to be conducted by CHMI. Tools are being developed for long-term prediction of water resource conditions and a methodology for drought and water scarcity management plans. These plans aim to ensure water supply, protect the environment, and minimize the economic impacts. The decision-making body for issuing measures based on the drought plans is the Drought Commission, which operates at the regional level. The warning information is available on the HAMR web portal, which also displays local threshold limits for individual water resources.
HAMR: online drought management system – web presentation to the public
Drought and water shortages are concepts that need to be spaced properly differentiate. Drought is a temporary decrease in water availability and is considered a natural phenomenon. Drought is characterized by its gradual onset, considerable area and long duration.
Update of empirical relationships for calculation of free water surface evaporation based on observation at Hlasivo station
Evaporation from free water surface is one of the essential components of water circulation in nature and significantly affects the overall water balance of the catchment. Due to the complicated direct measurement, it is often calculated from formulas that require available meteorological variables as input data.
HAMR: Online drought management system – operational management during a dry episode
Increasing occurrence of drought periods in the Czech Republic has highlighted a necessity of legislation modification. At the same time, a need has emerged for tools supporting decision making and water resources management at various levels during the drought periods.
Hydrological balance and available water resource in the czech republic during hydrological drought
The article deals with the assessment of the hydrological balance in a monthly time step in the territory of the Czech Republic, which was divided into 133 sub-basins for the period 1981–2015.
Regionalization of deficit runoff volumes in the Czech Republic
The aim of the study is the regionalization of the Czech Republic with respect to drought characteristics in individual catchments.
Quantifying the retention characteristics by the means of geomorphological patterns of the basin
In the presented study we tested the selected sets of linear and nonlinear regression models, that describe the relationships between the selected parameters of hydrological model Bilan, which were estimated using the meteorological, hydrological series, and between the retention characteristics estimated using the selected geomorphological patterns of the river basin.
Changes in the hydrological balance caused by climate change impacts in the Karlovy Vary district
In the Karlovy Vary district, areas with lack of drinking and industrial water were identified. Since 2015, in cooperation of TGM WRI, p. r. i., and state enterprise Povodí Ohře a project called „Increasing water resources availability in selected regions of Karlovy Vary district“ is financed
Bias correction of precipitation and temperature from regional climate models – the impact on runoff modelling
Hydrological modelling is often used for assessment of climate change impacts on water resources. Inputs into the hydrological model are represented by precipitation and temperature based on simulations of climate models.
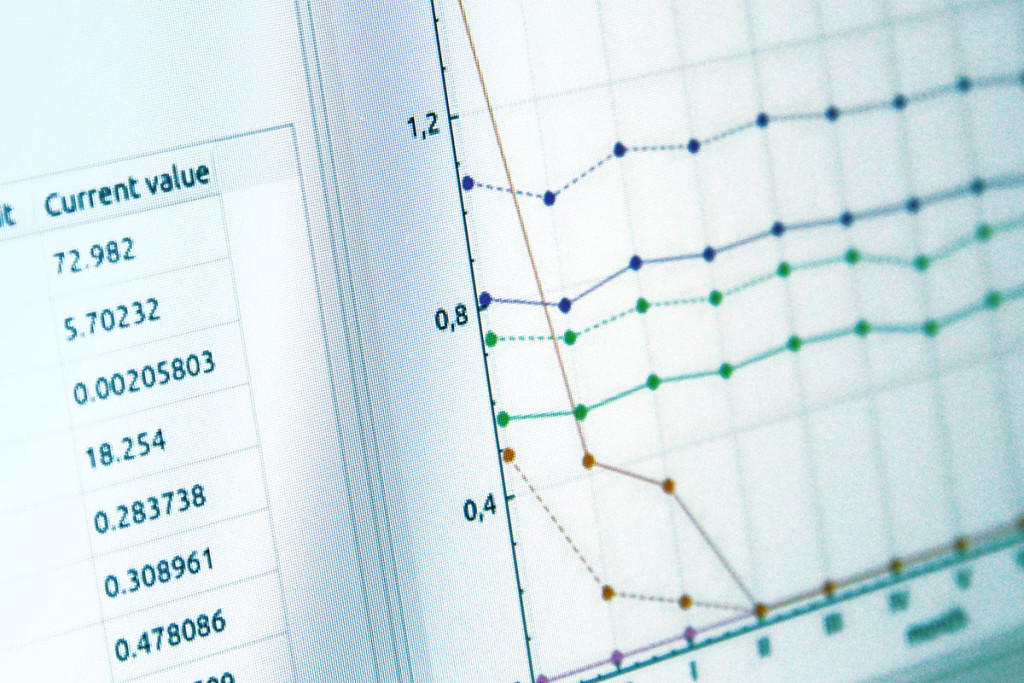
Recent developments of the BILAN model
The BILAN model has been used in a number of research projects and hydrological studies dealing with estimation of water balance for European catchments. This paper is focused on the recent development of the model during last years. The model changes include both core development (new variables representing water use, optional calibration for a system of catchments, saving of state variables) and enhanced user interface that was extended by new graphical outputs and controls allowing interactive use of the model.
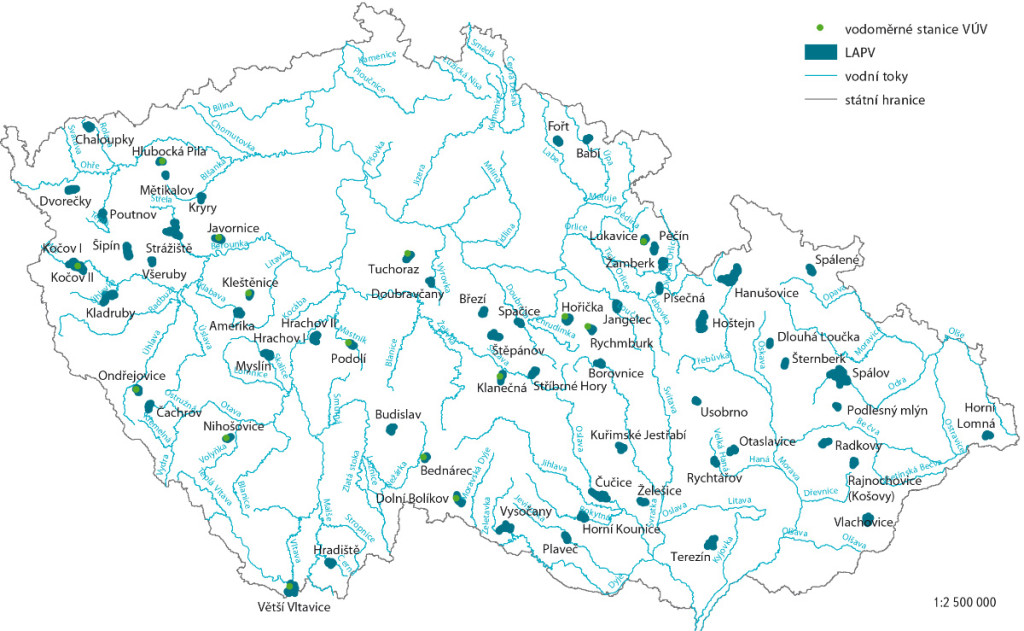
Possible compensation of negative climate change impacts using the localities for potential accumulation of surface water
The list of localities potentially suitable for accumulation of surface water (LASW) exists in the Czech Republic from the beginning of 20th century.
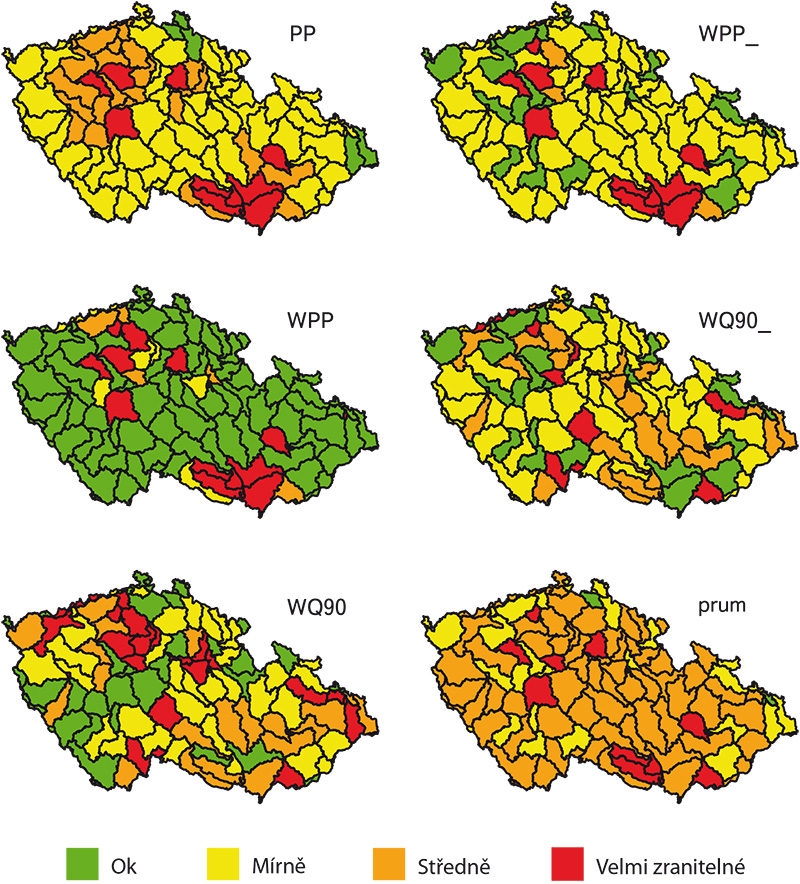
Identification of regions vulnerable to deficits in water resources in the Czech Republic
The article presents the applied methodology and description of the most important results achieved in the project.